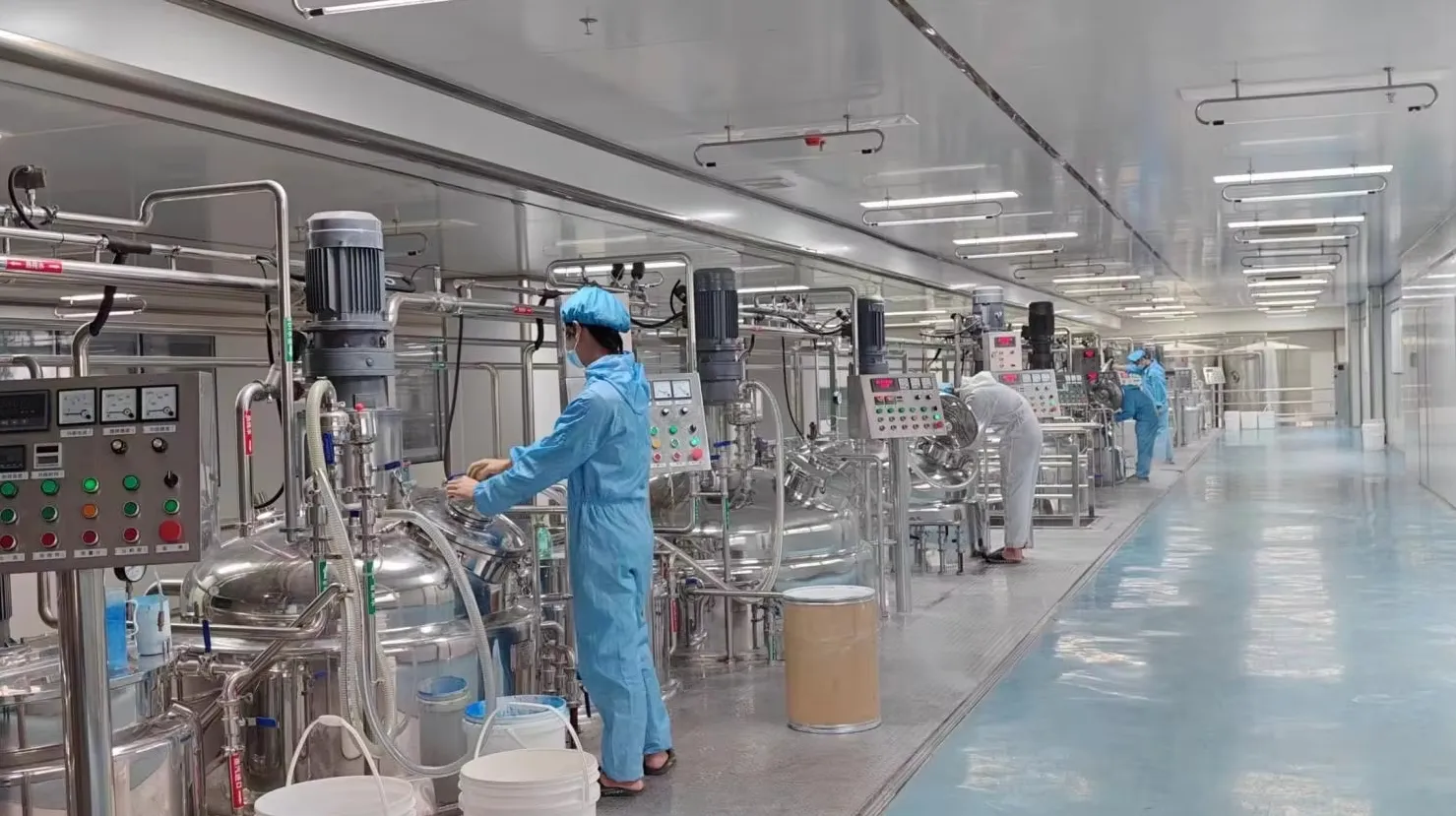
Toothpaste Manufacturing Process: A Complete Guide
Introduction to Toothpaste Manufacturing
Toothpaste is an essential oral hygiene product used globally to maintain dental health. The manufacturing process of toothpaste involves several technical and precise stages that ensure a safe, effective, and high-quality product. With millions of tubes produced each day, manufacturers must maintain stringent standards to ensure the product’s safety, efficacy, and consumer satisfaction.
This comprehensive guide outlines the critical steps involved in the toothpaste manufacturing process, from ingredient selection to packaging, while also discussing the key factors that impact product quality and safety. By the end of this guide, manufacturers will have a clear understanding of how toothpaste is produced and what factors must be considered for optimal product development.

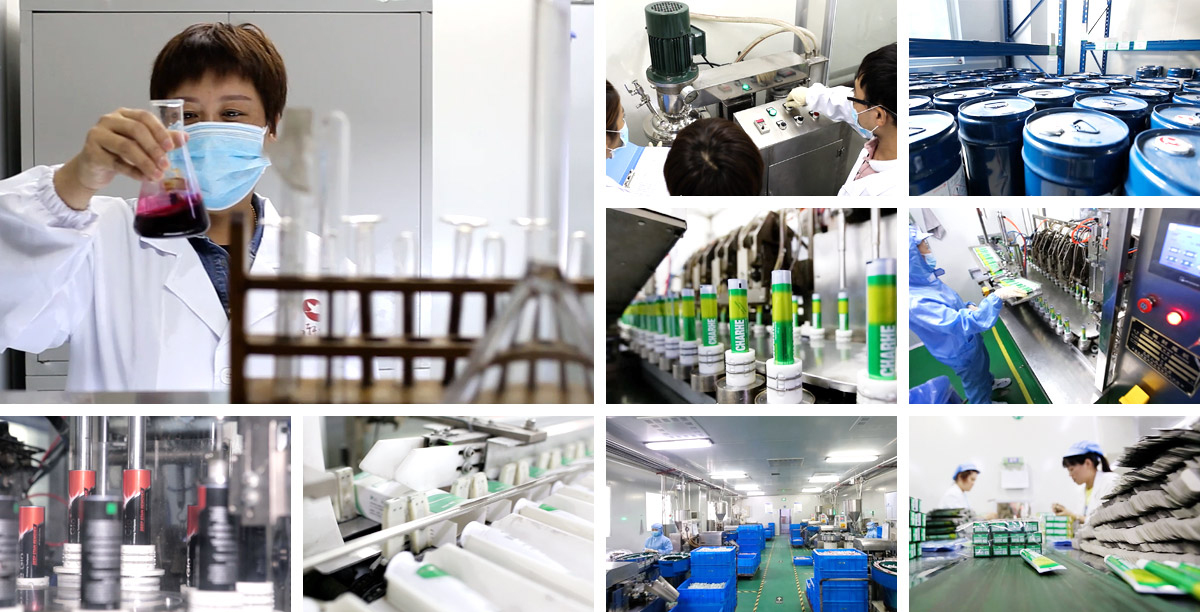
Key Ingredients in Toothpaste Manufacturing
Before delving into the production process, it’s important to understand the core ingredients that make up a typical toothpaste formulation. These ingredients are responsible for the toothpaste’s function, texture, and overall appeal to consumers.
Abrasives: Abrasives are responsible for the mechanical cleaning of teeth. These are key to removing plaque, tartar, and stains. Common abrasives include calcium carbonate, hydrated silica, and dicalcium phosphate dihydrate.
Binders: Binders are used to hold the toothpaste together and maintain its consistency. They prevent the product from separating and give it the desired texture. Examples include xanthan gum, guar gum, and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC).
Surfactants: These compounds aid in the spreading of the toothpaste and create the foam that consumers expect during brushing. Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is the most commonly used surfactant.
Fluoride: Fluoride is the active ingredient used in many toothpaste formulations for its cavity-fighting properties. Sodium fluoride and stannous fluoride are the most commonly used forms.
Humectants: Humectants are used to retain moisture and prevent the toothpaste from drying out. Glycerin and sorbitol are popular humectants in toothpaste formulations.
Flavoring Agents: Flavoring agents are added to improve the taste of the toothpaste. Peppermint, cinnamon, and spearmint are some of the most commonly used flavors.
Preservatives: These ingredients extend the shelf life of toothpaste and prevent microbial growth. Methylparaben and propylparaben are often used.
Water: Water serves as a solvent, dissolving various ingredients and ensuring the correct viscosity of the paste.
The Toothpaste Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process is divided into several key stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality product. The process typically includes ingredient preparation, mixing, quality control, filling, packaging, and distribution. Below, we’ll examine each stage in detail.
1. Ingredient Preparation
The first step in toothpaste manufacturing is to gather and prepare all raw ingredients. Each ingredient must meet strict quality standards to ensure that the final product is safe and effective. Ingredients are measured according to the formula developed by the research and development (R&D) team.
The preparation of ingredients can involve grinding, screening, and blending. For example, abrasives like calcium carbonate may need to be ground into a fine powder to ensure that the toothpaste has the right texture and cleaning effectiveness. Other ingredients, such as humectants and surfactants, are typically pre-mixed in separate batches before being added to the main formulation.
2. Mixing
Once all ingredients are prepared, the next step is to mix them together. This is a crucial stage in toothpaste production, as it ensures the even distribution of all ingredients and guarantees that the paste has the desired consistency. The mixing process typically follows these steps:
Phase Mixing: In the first phase, liquid ingredients such as water, humectants, and preservatives are combined. The liquid base is then blended with thickening agents, which include binders like xanthan gum.
Adding Powders: After the liquid phase, abrasives and fluoride compounds are added. This ensures that the active ingredients are well-dispersed throughout the toothpaste formulation.
Homogenization: The paste is then homogenized to ensure that the ingredients are uniformly distributed, with no lumps or inconsistencies. This ensures that each tube of toothpaste will have the same texture and fluoride content.
Adjusting Viscosity: The final step of mixing involves adjusting the viscosity of the toothpaste. The mixture is continuously monitored to ensure that it has the right thickness. This can be achieved by altering the speed or duration of mixing, or by adding more binder or humectant.
3. Quality Control Testing
Once the toothpaste mixture is ready, it undergoes a series of quality control tests to ensure it meets the necessary standards. These tests include:
Viscosity Testing: The toothpaste’s consistency is checked to ensure it is neither too runny nor too thick.
pH Testing: The pH of the toothpaste must be balanced, typically between 6 and 8, to ensure it is safe for oral use and does not cause irritation.
Flavor and Texture Evaluation: Consumer preference tests are conducted to ensure the toothpaste’s flavor and texture align with market demands.
Microbial Testing: To ensure the safety of the product, microbial testing is done to confirm that the paste is free from harmful bacteria and other microorganisms.
Fluoride Content Testing: A critical test is the verification of fluoride concentration to ensure that it aligns with recommended levels for cavity prevention.
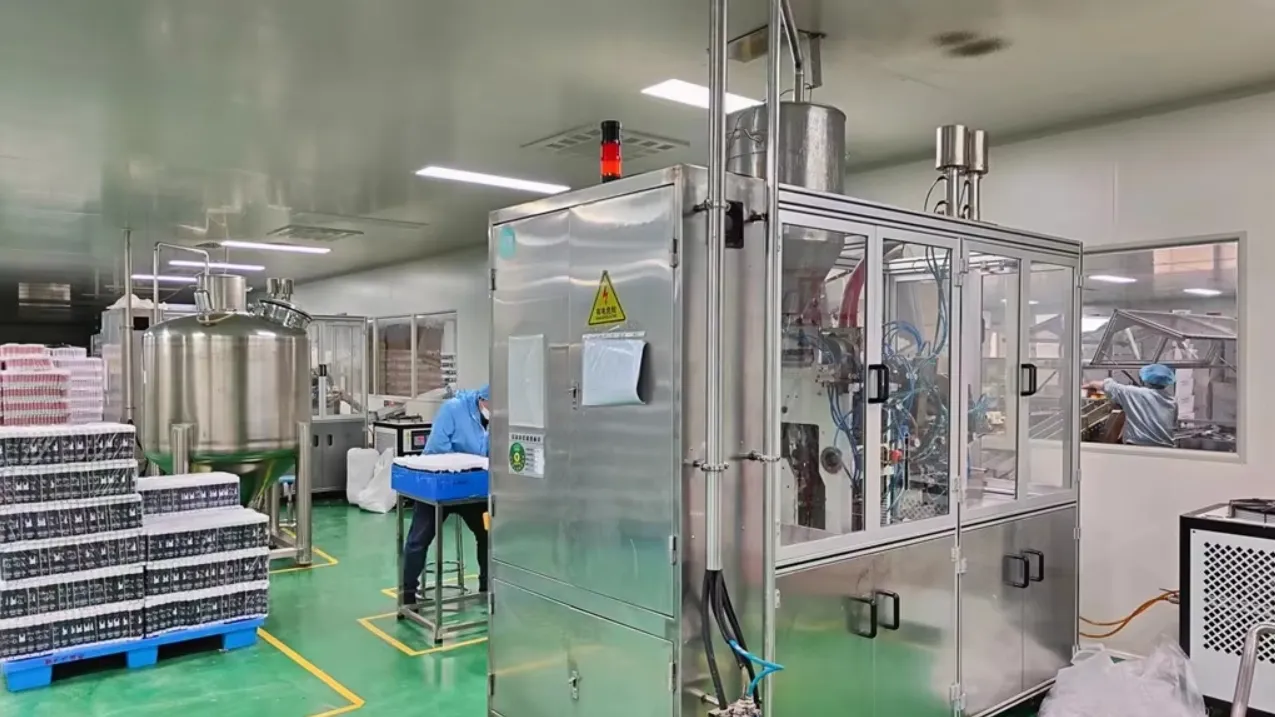
4. Filling and Packaging
After passing quality control tests, the toothpaste is ready for packaging. This stage involves several steps, including:
Filling: The toothpaste is transferred into pre-formed tubes or other packaging formats. Automated filling machines ensure that each tube receives the correct amount of product, which is important for product consistency.
Sealing: After filling, the tubes are sealed to preserve the integrity and freshness of the product. Heat sealing is typically used for plastic tubes, while metal tubes may be crimped.
Labeling: Labels are applied to each tube, including necessary product information, such as ingredients, usage instructions, and expiration dates. The labeling process also ensures that branding is consistent across batches.
Secondary Packaging: Finally, the sealed and labeled tubes are placed in secondary packaging, such as cartons or boxes, for distribution.
5. Distribution
Once packaged, the toothpaste is stored in climate-controlled warehouses to maintain freshness and stability. Manufacturers then distribute the product to wholesalers, retailers, or directly to consumers, depending on their business model.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Sustainability: Modern toothpaste manufacturers are increasingly focused on using eco-friendly packaging materials and responsibly sourced ingredients. Sustainable practices are becoming a key selling point for many consumers.
Regulatory Compliance: Toothpaste manufacturers must comply with regulations from health authorities such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), or other regional regulatory bodies. These regulations ensure the safety and efficacy of the product, particularly for active ingredients like fluoride.
Try Lidercare Now!
We Help You Launch New Products, And Continue To Grow. Try Us With 20% Off Your First Order!
Conclusion
The toothpaste manufacturing process is complex and requires a high degree of expertise and precision. Each stage, from ingredient preparation to packaging, plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product is safe, effective, and appealing to consumers.
By understanding the intricacies of toothpaste production, manufacturers can optimize their processes to create high-quality products that meet consumer needs. At Lidercare, we are committed to supporting manufacturers with top-tier raw materials and formulation expertise to ensure the highest standards in toothpaste production.
Table of Contents
Awesome! Share to:
Latest Blog Posts
Check out the latest industry trends and take inspiration from our updated blogs, giving you a fresh insight to help boost your business.